Enhancing Workplace Inclusion for Individuals with Chronic Illness and Disabilities in the UK
- Elevation Occ Psy

- Feb 17, 2025
- 7 min read
Introduction
Chronic illnesses and disabilities affect a significant portion of the UK workforce, with approximately 16 million people in the UK living with a long-term health condition or disability (ONS, 2022). Despite progress in workplace inclusion, many employees with chronic illnesses continue to face challenges that hinder their full participation. Creating inclusive workplaces is essential for fostering a diverse, equitable, and productive workforce (Scope, 2021).
Elevation Occ Psy is committed to promoting inclusion, respect, and advocacy for individuals with chronic health conditions and disabilities. Our mission is to support organisations in implementing effective strategies that enhance accessibility, well-being, and professional growth for all employees.
1: Understanding the Current Landscape
The landscape of employment for individuals with chronic illnesses and disabilities is complex and multifaceted. With millions affected, it's crucial to understand the current state of inclusion and the challenges faced by these individuals in the workplace. Here we highlight the prevalence of chronic conditions and disabilities in the UK workforce, examining employment rates and workplace barriers. By understanding these dynamics, organisations can better address the needs of their employees and create a more inclusive environment.
Prevalence and Employment Trends
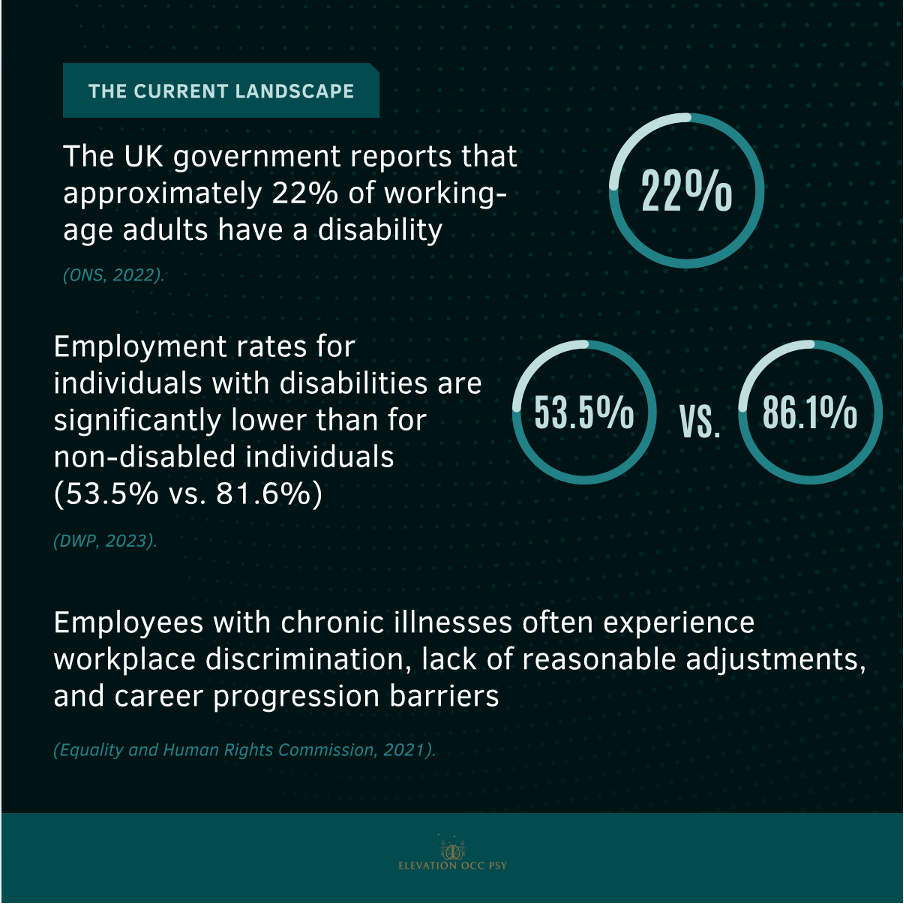
The prevalence and employment trends for individuals with disabilities in the UK reveal significant disparities and challenges. According to the Office for National Statistics (ONS, 2022), around 22% of working-age adults have a disability. Despite this substantial portion of the population, employment rates for individuals with disabilities remain significantly lower than those for non-disabled individuals, with only 53.5% of disabled individuals employed compared to 81.6% of their non-disabled counterparts (DWP, 2023). This gap underscores systemic issues within workplaces, where employees with chronic illnesses frequently encounter discrimination, inadequate reasonable adjustments, and barriers to career progression (Equality and Human Rights Commission, 2021). These challenges highlight the urgent need for inclusive policies and practices that support and empower individuals with disabilities, ensuring equal opportunities for employment and advancement.
Workplace Challenges

Workplace challenges for individuals with chronic illnesses and disabilities are multifaceted and deeply rooted in systemic issues. One significant barrier is the limited access to flexible work arrangements, which can be crucial for employees managing health conditions (TUC, 2022). This lack of flexibility often stems from insufficient employer awareness and understanding of the unique needs associated with chronic illnesses (CIPD, 2021). Furthermore, unconscious biases continue to permeate hiring and promotion processes, adversely affecting the opportunities available to these individuals (Business Disability Forum, 2020). These challenges not only hinder personal and professional growth for employees with disabilities but also limit the potential for diverse and inclusive workplace environments. Addressing these issues requires a concerted effort to educate employers, implement flexible policies, and actively work to eliminate biases, thereby fostering an inclusive culture where all employees can thrive.
2: Barriers to Inclusion
Despite advancements in awareness and policy, significant barriers remain for employees with chronic illnesses and disabilities. These barriers can be physical, social, or organisational, impacting both individual well-being and overall workplace productivity. Here we delve into the various barriers faced by employees, including stigma and lack of awareness. Through case studies, we explore the real-world impact of these challenges and emphasise the need for comprehensive strategies to overcome them
Physical, Social, and Organisational Barriers

Physical, social, and organisational barriers present significant challenges for employees with chronic illnesses and disabilities, impacting their ability to thrive in the workplace. Physically, many office environments remain inaccessible, lacking ergonomic accommodations and essential assistive technologies, which are vital for creating an inclusive workspace (EHRC, 2021). Socially, employees often face stigma, insufficient peer support, and exclusion from social activities, which can lead to feelings of isolation and hinder their professional engagement (Scope, 2021). Organisationally, rigid policies, inadequate sick leave provisions, and the absence of structured support mechanisms further exacerbate these challenges, making it difficult for individuals to balance their health needs with work responsibilities (CIPD, 2021). Addressing these barriers requires a comprehensive approach that includes redesigning physical spaces, fostering a supportive social environment, and implementing flexible organisational policies to ensure all employees can contribute fully and equally.
The Impact of Stigma

The impact of stigma in the workplace is profound and far-reaching, particularly for employees with chronic illnesses and disabilities. Stigma can significantly lower employee engagement, increase stress levels, and contribute to higher turnover rates, as individuals feel unsupported and undervalued (Mental Health Foundation, 2022). The fear of discrimination often deters employees from disclosing their health conditions, leading to a lack of necessary accommodations and support (TUC, 2022). For instance, a case study from the Business Disability Forum (2020) illustrates how an employee with an autoimmune disease faced fluctuating symptoms without adequate employer support, ultimately resulting in burnout and resignation. This highlights the critical need for workplaces to actively combat stigma by fostering an environment of understanding and support, where employees feel safe to disclose their conditions and receive the accommodations they need to thrive.
3: Strategies for Creating Inclusive Workplaces
Creating an inclusive workplace requires intentional strategies and practices that support employees with diverse needs. Employers play a pivotal role in fostering an environment where everyone can contribute fully. Here we outline best practices for employers, including the use of psychological assessments, training, and education to enhance inclusion. By adopting these strategies, organisations can build a culture that values diversity and supports all employees
Best Practices for Employers

Adopting best practices for supporting employees with chronic illnesses and disabilities is essential for creating an inclusive and thriving workplace. One of the most effective strategies is implementing flexible work policies, such as remote work options and adjustable hours, which can accommodate the diverse needs of employees managing health conditions (CIPD, 2021). Additionally, developing clear and comprehensive reasonable adjustment policies is crucial for addressing individual needs and ensuring that all employees have the necessary support to perform their roles effectively (EHRC, 2021). Equally important is fostering an open and supportive culture where employees feel safe and encouraged to discuss health-related concerns without fear of discrimination or judgment (TUC, 2022). By embracing these practices, employers can significantly enhance workplace inclusion, promote well-being, and boost overall productivity.
Role of Psychological Assessment

The role of psychological assessment in the workplace is pivotal in creating an environment that supports individuals with chronic illnesses and disabilities. Occupational psychologists have the expertise to assess workplace needs and recommend tailored adjustments that accommodate individual requirements, enhancing both employee satisfaction and productivity (BPS, 2021). These assessments can identify specific stressors and the necessary support mechanisms, allowing organisations to implement strategies that reduce stress and promote well-being (Mental Health Foundation, 2022). By integrating psychological assessments into workplace practices, employers can foster a more inclusive and supportive environment, ultimately contributing to the overall success and resilience of their workforce.
Training and Education

Training and education are fundamental components in fostering an inclusive workplace, particularly for employees with disabilities and chronic health conditions. Regular diversity and inclusion training, with a focus on disability awareness, is essential for building understanding and empathy among staff, thereby reducing stigma and enhancing workplace culture (Scope, 2021). Leadership training plays a crucial role in equipping managers with the skills needed to create supportive and adaptive work environments that cater to the diverse needs of all employees (CIPD, 2021). Additionally, establishing employee resource groups can significantly enhance peer support and advocacy, providing a platform for employees to share experiences, resources, and strategies for navigating workplace challenges (Business Disability Forum, 2020). By investing in these training and educational initiatives, organisations can cultivate a more inclusive and supportive environment that empowers all employees to thrive.
4: Empowering Employees and Employers
Empowerment is key to achieving workplace inclusion. By providing the right resources and support, both employees and employers can work together to create a thriving workplace. Here we focus on empowering individuals through advocacy, policy changes, and supportive workplace structures
Resources for Well-being and Productivity

Resources for well-being and productivity are vital in supporting employees with chronic illnesses and disabilities, ensuring they can contribute fully and effectively in the workplace. Providing mental health support and resilience training is essential for helping employees manage stress and maintain their mental well-being, which is crucial for sustained productivity (Mental Health Foundation, 2022). Access to assistive technologies and workplace accommodations further empowers individuals by enabling them to perform their tasks efficiently and comfortably (EHRC, 2021). Additionally, establishing mentorship programs can significantly enhance career development, offering guidance, support, and opportunities for growth, while fostering a sense of community and belonging (BPS, 2021). By integrating these resources, organisations can create a nurturing environment that supports the well-being and productivity of all employees.
Advocacy and Policy Change

Advocacy and policy change are crucial in driving the transformation towards more inclusive workplaces, particularly for individuals with chronic illnesses and disabilities. Encouraging organisations to adopt inclusive recruitment and retention policies is a fundamental step in ensuring that all employees, regardless of their health conditions, have equal opportunities for employment and advancement (DWP, 2023). Promoting compliance with the Equality Act 2010 further safeguards employee rights, providing a legal framework that supports fairness and equality in the workplace (EHRC, 2021). Engaging in industry-wide advocacy is essential to normalise workplace inclusivity, fostering a culture where diversity is not only accepted but celebrated (Scope, 2021). Through these efforts, organisations can create a more equitable and supportive environment, paving the way for a future where all employees can thrive.
Conclusion
Creating inclusive workplaces for individuals with chronic illnesses and disabilities is not just a legal obligation but a moral and strategic imperative. Organisations that embrace inclusivity benefit from a more engaged workforce, improved productivity, and enhanced company reputation (TUC, 2022).
Elevation Occ Psy urges employers to take actionable steps towards fostering supportive work environments. By prioritising accessibility, understanding, and proactive policy changes, businesses can drive meaningful change and support the long-term success of all employees.
References
Business Disability Forum (2020). Disability-Smart Inclusive Leadership Guide.
British Psychological Society (BPS) (2021). Workplace Adjustments for Employees with Disabilities.
Chartered Institute of Personnel and Development (CIPD) (2021). Disability Inclusion in the Workplace.
Department for Work and Pensions (DWP) (2023). Labour Market Statistics.
Equality and Human Rights Commission (EHRC) (2021). Workplace Adjustments: Employer Responsibilities.
Mental Health Foundation (2022). The Impact of Workplace Stigma on Mental Health.
Office for National Statistics (ONS) (2022). Disability and Employment Statistics.
Scope (2021). The Disability Perception Gap.
Trades Union Congress (TUC) (2022). Disability Employment and Workplace Support.




Comments